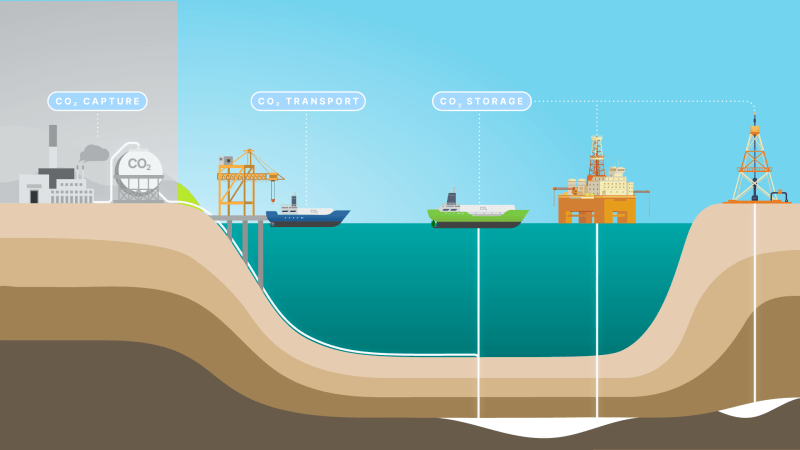
How Does Carbon Capture Work – Carbon storage (CCS) works by capturing the carbon dioxide (CO2) released by burning fossil fuels in power plants and other industrial environments and storing it deep underground. Current CCS technologies can capture 90 percent or more of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to significantly reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations below this threshold.
Figure 1: An industrial plant that stores carbon dioxide in a warehouse and releases it into the atmosphere
How Does Carbon Capture Work

The introduction of renewable energy sources such as solar technology and the goal of introducing carbon-free energy sources to others is no longer excluded, but it is still not enough to lower the CO2 threshold of our environment to an optimal level. level. Something else is needed to remove the CO2 that has already accumulated in the environment. Here, CCS technology is able to sequester carbon dioxide in applied environments such as cryogenics, forestry, etc.
Tgrc Limited T/a The Green Recruitment · Green Recruitment Company
According to our research report, CCS technology has the ability to capture 90% of the carbon dioxide that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. This amazing success is not for lack of success. Although CCS has great potential, large-scale deployment remains expensive, and these significant financial costs have made large industrial companies reluctant to invest in the technology. This is because more energy is used to perform these tasks instead of producing carbon dioxide, which reduces the overall efficiency of the operation.
CCS technology can help achieve the goal of a clean energy environment with less CO2 emissions in the environment, as coal fuels still play an important role in our energy supply, and CCS will play an important role for many years to come. In reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Public support remains essential for the widespread adoption of CCS. CCS is produced in power plants and other industrial plants, which typically release emissions into the atmosphere and contribute to global warming. Carbon dioxide captured by any of these methods is captured for other purposes or stored in a place where it cannot escape. This process is known as carbon sequestration.
Post-combustion carbon recovery: This technology, most commonly used today, releases smoke, a toxic gas, before releasing it into the air. In a technique called adsorption or desorption, pollutants are delivered to a device called an absorber, where the carbon dioxide interacts with a chemical solvent that absorbs and releases it. The carbon dioxide and solvent are then separated so that the solution can be reused, after which the carbon dioxide is compressed, transported and stored.
Oxide Fuel Combustion: In this type of recovery, the fuel is burned in an atmosphere close to pure oxygen rather than normal air, producing high concentrations of easily collected carbon dioxide.
What Happens To Carbon Stored Underground?
Direct air capture: Unlike the first three methods, where emissions occur at the source, direct air capture attempts to remove carbon dioxide from the air wherever it is. For this, the giant fans suck air into a device called a manifold, where carbon dioxide is separated in the same way as in an afterburner. The technology is still in the experimental phase.
After successfully capturing carbon dioxide, the next question is how to do it? One option is to store or recycle it, which may not harm the atmosphere. There are two types of storage: geological and biological.
Geological storage: In geological storage, captured carbon dioxide is heated and then pressurized into “super” carbon dioxide and injected deep underground. As explained by the US Department of Energy, unusual CO

“Certain properties like a gas and certain properties like a liquid. In particular, it is dense like a liquid but has a viscosity like a gas. The main advantages of CO storage are:
Ccs Explained: Storage
Biostorage: Biostorage depends on natural processes to capture and store carbon dioxide, such as forest plantations where trees and other plants absorb and store it and produce oxygen during photosynthesis.
Instead of capturing and storing carbon dioxide through the process of carbon capture and storage (CCS), some technologies allow it to be used in production – this is called carbon capture, use and storage (CCUS).
Some of the captured carbon dioxide is pumped into oil wells as a way to “displace hard-to-produce oil,” according to MIT’s Environmental Solutions Initiative. In addition, it helps plants grow in some greenhouses. Other possible uses include conversion to CO
“Construction materials like plastics, cement and concrete, fuels, future materials like carbon fiber and graphene, and even household products like baking soda, bleach, antifreeze, ink and paint.” None of them are in mass production.
Three Organisations Teaming Up To Unlock Uk’s Full Carbon Capture And Storage Potential
The main advantage of carbon sequestration is that it has the potential to slow down and restore the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere, which is the main cause of global warming, climate change and all the associated dangers.
The main disadvantage at this stage is the cost, especially the cost of scaling, which has many consequences. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s 2023 report states that carbon capture is one of the most effective and cost-effective ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, far ahead of alternatives such as wind, solar, geothermal and nuclear power.
A related concern is that the emphasis on carbon capture is an unnecessary shift away from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. As the 2021 essay

In other words, “Hype, news, and hype lead to the belief that carbon emissions are cheap, easy, scalable, and reliable, which we can’t wait for.”
Global Forest Coalition The Phantom Of The Cop21 Opera: Bioenergy With Carbon Capture And Storage
The campaign group Food and Water Watch is more blunt: “Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is the biggest plan in the fossil fuel industry to date, and it has failed to convince people that the climate crisis can still be solved by selling. He calls CCS a “fake,” “snake oil,” a “scam” and a “sales pitch.”
By 2030, solar and wind will be the largest sources of net emissions reductions, followed by coal, oil and natural gas.
Coal recovery dates back to at least the 1920s, when oil and gas drillers began absorbing carbon dioxide as a commodity gas. But it seems to have become more common in the 1970s when drillers began pumping it into oil wells to help recover the oil. This is called enhanced oil recovery.
This idea gained some traction in the 1980s and 1990s, when the environmental effects of carbon dioxide became more widely known. Despite this, development was slow. Today, there are about 40 commercial CCUS plants worldwide, with “over 500 projects in various stages of development” according to the International Energy Agency.
How Amc Is Fighting Climate Change Through Carbon Credits
Although there are many critics of carbon sequestration, others see it as at least a useful temporary measure. According to the International Energy Agency, the CCUS system “can be retrofitted to existing power and industrial facilities to allow them to continue operating. “It can handle pollutants from complex industries, particularly heavy industries such as cement, steel and chemicals.” The organization says CCUS can also “remove CO
An article on the World Economic Forum website states: “Climate scientists say net-zero carbon goals unlikely to be met unless CCUS is adopted globally.” But, he adds, “the shortcomings of these technologies, including high technology and low efficiency, must be addressed before CCUS can be widely adopted and become an effective climate solution.”
In the United States, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021 provided more than $12 billion for CCUS projects, and these funds are being used slowly. For example, in August 2023, the Department of Energy (DOE) announced a $1.2 billion investment in two commercial direct air recovery facilities, one in Louisiana and one in Texas. The Energy Department said the funding “is intended to enable a large-scale carbon emissions network around the country to address carbon pollution and offset accelerated emissions.”

Idea Carbon recovery is one of several ways to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Proponents say it’s the best way to modernize existing industrial plants so they pollute less by burning fossil fuels. Opponents think it would be better if the factories switched to renewable energy sources. However, carbon capture can be a good idea, as in this case, until it is economically feasible.
Why Is Carbon Important?
Carbon sequestration is slow for several reasons. One of them is cost, and unless the government forces polluters to do so, or unless the government gives them financial incentives, they have no reason to do so.
How does carbon credits work, how to capture carbon dioxide from air, what does carbon capture mean, how does carbon dating work, how does carbon pricing work, how carbon capture works, how does carbon sequestration work, how does carbon capture and storage work, how does carbon trading work, how to capture carbon, how to capture carbon dioxide, does carbon capture work