Earth Spinning On Its Axis Is Called – The rotation of the Earth or the rotation of the Earth is the rotation of the Earth on its axis and the change in the position of the axis of rotation. The earth turned eastwards in a progressive movement. The Earth rotates counterclockwise as seen from the North Pole.
The North Pole, also called the north pole or terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth’s axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is different from the Earth’s North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is another point where the Earth’s axis of rotation crosses the surface of Antarctica.
Earth Spinning On Its Axis Is Called

Earth orbits the Sun every 24 hours, and other distant stars every 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (see below). The Earth’s rotation slows down a little over time. So the day was short. This is due to the tidal effects of the Moon on the rotation of the Earth. Atomic clocks show that today’s day is about 1.7 milliseconds longer than it used to be.
How Earth’s Orbit And Axis Cause Seasonal Changes
Slowly increases the speed, adjustable in UTC seconds. Historical analysis of astronomical records indicates a trd recession; After the 8th century BC, daylight increased by about 2.3 thousand seconds per light century.
After decades of rotating at a slower rate than 86,400 seconds per day, scientists say the Earth started spinning faster in 2020. On June 29, 2022, the Earth completed its rotation in 24 hours in 1.59 milliseconds, setting a new record.
This increase in speed is believed to be due to a variety of factors, including the complex dynamics of the core, the influence of the ocean, atmosphere, celestial bodies such as the Moon, and climate change causing ice at the Earth’s poles. . To melt the spherical shape of the Earth, the ice sheets are surrounded around the equator. As these masses decrease, the weight loss causes the poles to break away and the Earth becomes spherical, which has the effect of drawing the masses closer to their own gravitational field. By conserving angular momentum, the mass is more densely distributed around its center of gravity and spins faster.
This long exposure photograph of the northern night sky above the Nepalese Himalayas shows the unusual paths of the stars as the Earth rotates.
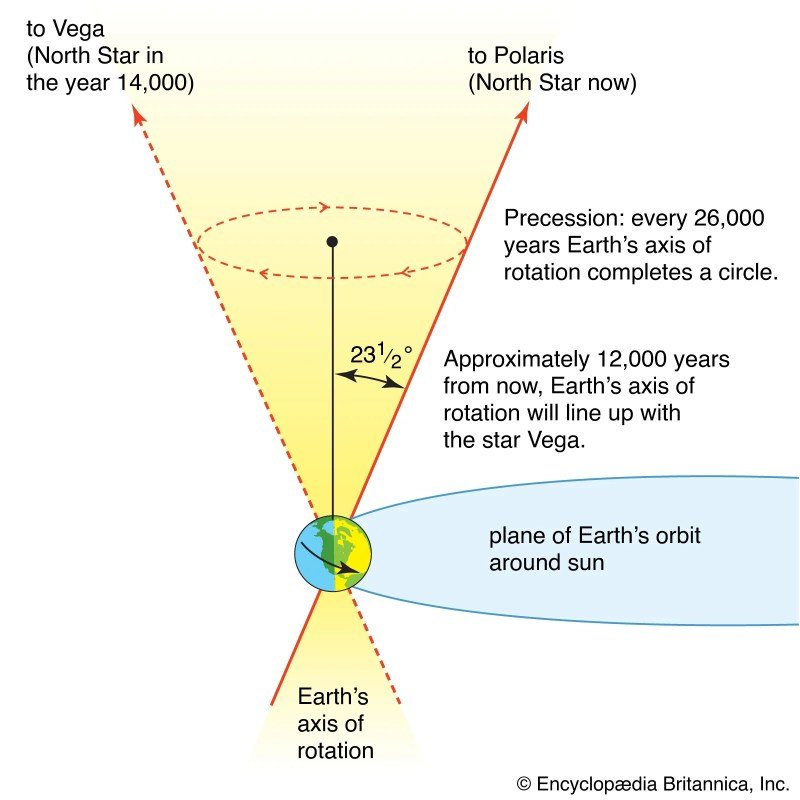
Earth’s Axis Has Secretly Shifted
Among the ancient Greeks, most of the Pythagorean school believed in the rotation of the Earth rather than the cycle of diurnal motions. Perhaps the first Philola (470-385 BC), although his system was complicated, even turned coal around the central fire every day.
A conventional picture supported by Hesedas, Heraclides, and Ecphantes in the fourth century BC assumed that the Earth rotates, but did not say that the Earth revolved around the Sun. In the third century BC, Aristarchus Samius proposed the location of Sol.
But in B.C. the fourth Aristotle was more critical of Philolaus’ theory than observational. He created the idea of a sphere of fixed stars revolving around the earth.

Most of his followers accepted this, at first Claudius Ptolemy thought that if the earth rotated, it would be destroyed by the wind.
How Does Earth Orbit The Sun?
In 499, the Indian astronomer Aryabhata hypothesized that the Earth rotates on its axis every day and that the relative motion of the stars depends on the rotation of the Earth. He continued with this simile: “As a man sailing in one direction sees a fixed one on the shore moving in the opposite direction, so a man in Ceylon sees the fixed stars in the west.”
According to al-Biruni, al-Sijzi (1020 CE) invented an astrologer called az-zuraq — who, according to some contemporaries, believed that “the motion we see” was not that of the heavens, but that of the earth. “
The prevalence of this view is further proved by a 13th century inscription: “The earth is in constant circular motion according to the earth (mukhantisin) and it appears to be the motion of gravity.” Not the movement of the earth. stars”.
Essays were written that refuted Ptolemy’s arguments or questioned their veracity.
Earth’s Rotation Day 2024: Date, Theme, History, Significance, Facts, & More
Tusi (b. 1201) and Khushji controlled the rotation of the earth in the Maraga and Samarkand observatories; arguments and are similar to those used by Copernicus.
In structure iii. Only after Nicolaus Copernicus formulated the heliometric system of the world in 1543, the current understanding of the rotation of the Earth was formed. Copernicus shows that if the motion of the earth is strong, the motion of the stars must be very great. He acknowledged the contribution of the Pythagoreans and gave examples of relative motion. For Copernicus, this was the first step in creating a simple system of planets orbiting the Sun.
Tycho Brahe, who published detailed observations on which Kepler based his Laws of Planetary Motion, used the work of Copernicus as a basis for predicting a stable Earth system. In 1600, William Gilbert strongly supported the rotation of the Earth in his Treatise on the Earth’s Magnetism.

People like Gilbert who neither fully support nor deny the motion of the Earth around the Sun are called “quasi-Copernicans”.
Humans Contribute To Earth’s Wobble, Scientists Say
After Copernicus, Riccioli argued for a model of the Earth’s rotation, since the fallen bodies had no significant eastward deviations;
Then the fluctuations are called the Coriolis effect. However, the contributions of Kepler, Galileo, and Newton provided support for the theory of the Earth’s rotation.
The rotation of the Earth means that the noses of the equator and the geographic poles are flat. In his Principia, Newton predicted that this explosion would be part of 230, and cited measurements taken by Richter in 1673 to confirm the change in gravity;
But early measurements of meridian longitudes by Picard and Cassini in the 17th century proved otherwise. However, in 1730, measurements made by the Maupertue and Frech geodetic mission determined the tilt of the Earth, thus confirming both Newton’s and Copernicus’ positions.
How Fast Does The Earth Spin?
In the Earth’s rotating reference system, a freely moving body follows a certain path that deviates from its path in a stationary reference system. Due to the Coriolis effect, objects falling from a vertical plume are inclined slightly below the point of launch, and projectiles tend to land to the right in the Northern Hemisphere (and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere) in the direction they were normally fired. The Coriolis effect is more pronounced at the meteorological level and is responsible for the circulation of cyclones in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres (counterclockwise and respectively).
In 1679, following Newton’s advice, Hooke made an unsuccessful attempt to verify the eastward tilt of a body dropped from a height of 8.2 meters, but later definitive results were obtained by John Baptista Guglielmo in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Johannes Friedrich Bisberg in Bonn, Hamburg and Ferdinand Reich in Freiburg carefully printed the weights using tall towers.
A ball dropped from a height of 158.5 m leaves a vertical 27.4 mm compared to the calculated value of 28.1 mm.

Foucault’s dome, the most famous experiment of the Earth’s rotation, was first constructed in 1851 by physicist Léon Foucault from a lead-coated sphere 67 m above the Panthéon in Paris. Due to the rotation of the tilted ground under the pdule, the plane of oscillation of the pdule rotates with a velocity relative to the latitude. The predicted and observed change in Paris latitude was 11 per hour clockwise. Foucault bottles are now imported as souvenirs around the world.
What Is Earth’s Axial Tilt?
The period of Earth’s rotation about the Sun (noon to noon) is the true solar day or apparent solar day.
It calculates the Earth’s orbital motion and accounts for changes in the Earth’s orbit and inclination. Each varies over a thousand years, so the annual variation of the actual solar day also varies. It is usually longer than the average solar day at two times of the year and shorter at the other.
A true solar day TDS is longer near perihelion, when the Sun moves through the ecliptic at a greater angle than usual, so it passes through the ecliptic in about 10 seconds. By contrast, it’s about 10 seconds shorter near Abilene. It’s about 20 seconds longer near the solstice, when the precession of the Sun’s apparent motion across the sky across the equinox moves the Sun at a greater angle than usual. On the other hand, near the equinox, the equinox prediction is about 20 seconds shorter. Short perihelion and solstice effects add only 30 seconds to the true solar day near December 22nd, but the ecliptic effect is partially offset by an aphelion effect of only 13 seconds near June 19th.