What Are Retained Earnings In Accounting – A statement of retained earnings (retained earnings statement) is a financial statement that shows changes in a company’s retained earnings over a certain period of time. This statement reconciles the opening and closing retained earnings for the period, uses information such as net income from other financial statements, and is used by analysts to understand how a company’s profits are being used.
The statement of retained earnings is also called the statement of equity, statement of equity, or statement of shareholders’ equity. Retained earnings statement boilerplate templates are available online. It has been prepared in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
What Are Retained Earnings In Accounting

This retained earnings statement can be a separate statement or line item on the balance sheet or income statement. A statement is a financial document that contains information about a company’s retained earnings, net income, and amounts distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. An organization’s net income is recorded, showing the amount set aside to cover certain obligations in addition to paying dividends to shareholders, as well as the amount to cover losses. Each statement covers a specific period of time as specified in the statement.
Chapter 15 Retained Earnings.
These funds are also called joint income, joint income, or joint income. These retained funds are often used to repay debt or are reinvested to encourage growth and development of the company.
Whenever a company generates excess returns, some long-term shareholders may expect regular returns in the form of dividends in return for investing their money in the company. Traders looking for short-term profits may prefer dividend payouts that provide immediate profits. Dividends are paid out of profits, thus reducing a company’s retained earnings.
The following options cover several possibilities for how you can use excess cash that would normally be allocated to retained earnings and not paid out as dividends.
The purpose of issuing a retained earnings statement is to increase market and investor confidence in the organization. It is used as an indicator to help analyze the health of a company. Retained earnings are not the same as surplus. Instead, retained earnings are often utilized by being reinvested in the organization.
Odoo Closing Entries
Typically, retained earnings in capital-intensive industries or growing companies will be higher than in less intensive or stable companies. This is because more money is diverted towards asset development. For example, a technology-based company may have higher asset development needs than a simple t-shirt manufacturer due to the difference in focus on developing new products.
While a t-shirt can remain essentially unchanged for a long period of time, a computer or smartphone requires more constant evolution to remain competitive in the marketplace. Therefore, a technology company is likely to have higher retained earnings than a t-shirt manufacturer.
One of the financial data that can be obtained from the retained earnings statement is the retention ratio. The retention ratio (or retention ratio) is the percentage of earnings that are kept back in the business as retained earnings. Retention ratio refers to the percentage of net profits that are retained for business growth rather than being paid out as dividends. Dividend is the opposite of payout ratio, which measures the proportion of profits paid out to shareholders as dividends.

The retention ratio helps investors determine how much money the company is retaining to reinvest in the company’s operations. If a company does not pay out all of its retained earnings as dividends or reinvests them in its business, profit growth may suffer. Additionally, companies that do not use their surplus effectively are more likely to take on additional debt or issue new stock to finance growth.
What Are Income Tax Basis Financial Statements?
As a result, the retention rate helps investors determine the company’s reinvestment rate. However, businesses that retain too much of their profits may not be using their funds effectively, and that money may be better invested in new equipment, technology, or product line expansion. New companies typically do not pay dividends because they are still growing and need capital to finance growth. However, established companies typically pay out a portion of their retained earnings as dividends and a portion is reinvested into the company. If you run a small business, it’s important to have extra cash available to invest or pay off debt. But with money constantly coming in and going out, it can be difficult to keep track of how much money you have left. Use your retained earnings account to track your business’s accumulated totals.
Knowing your business’s retained earnings can help you make decisions and raise financing. Learn what retained earnings are and how to calculate and record them.
Retained earnings are business profits that can be used to invest or repay business debt. Retained earnings represent the amount remaining after paying expenses and dividends to shareholders or business owners. Retained earnings are also called retained earnings or retained earnings.
Retained earnings must be reported at the end of each accounting period. Common accounting periods include monthly, quarterly, and annual. You can compare a company’s cumulative profits from one accounting period to another.
Retained Earnings And The Expanded Accounting Equation
So what goes into retained earnings? To calculate retained earnings, you need to know your business’s previous retained earnings, net income, and dividends.
You can find your business’s previous accumulated profits on your business balance sheet or retained earnings statement. Your company’s net profit can be found in its income statement or profit and loss statement. If you have shareholders, the dividends you pay are the same as if you paid them.
If you are a new business and have never maintained income before, enter $0. And if you previously had negative retained earnings, make sure you label them correctly.

Can retained earnings be negative? Retained earnings may become negative if the net loss and initial retained earnings are low or negative.
Closing Entry In Accounting For Dummies: Definition, Example, And Best Practices
On the other hand, if you have net income and significant retained earnings, your retained earnings may be positive.
Let’s say you start with $25,000 in retained earnings. Your net income for this accounting period is $30,000. And pays dividends of $20,000.
Now let’s look at an example of negative retained earnings. You maintained an initial income of $4,000 and a net loss of $12,000. No dividends were paid.
Your business has a deficit of $8,000. Retained earnings are cumulative, so you should use -$8,000 as retained earnings to start the next accounting period. You need high net income to get out of that hole.
Calculation Of Cost Of Retained Earnings
When you create a journal entry to increase or decrease an income or expense account, you must adjust the retained earnings account.
Is retained earnings an asset? Actual retained earnings are reported in the equity section of the balance sheet. Retained earnings can be invested in assets, but they are not assets themselves.
Retained earnings must be recorded. Typically recorded in the equity section of the balance sheet. However, you can record retained earnings in a separate financial statement called the retained earnings statement.

The balance sheet is divided into three parts: assets, liabilities, and equity. The Assets section displays valuable items your business owns. The liability section will show you how much you owe. And the assets section shows how much money you have left after paying off your debts.
How Are The 3 Financial Statements Linked? (income Statement, Balance Sheet, And Cash Flow) And Why It Matters!
On the balance sheet, retained earnings appear under the “Equity” section. “Retained Earnings” is a line item that helps determine total business capital.
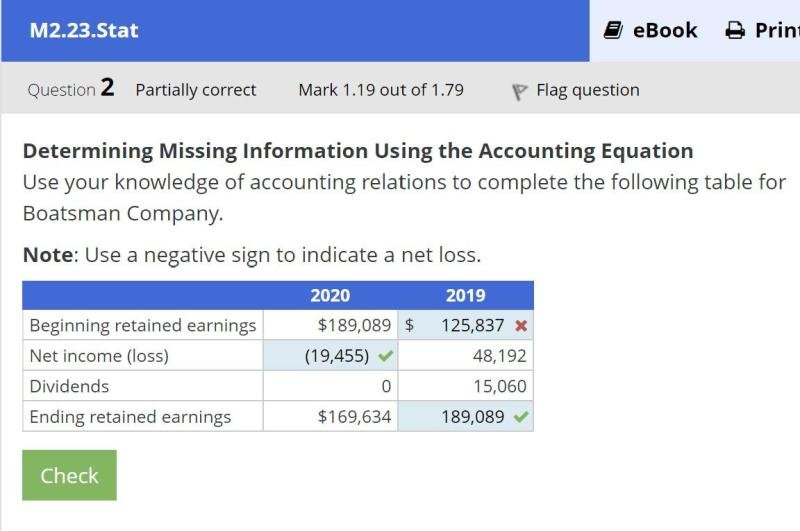
The retained earnings statement is a financial statement that focuses solely on calculating retained earnings. Similar to the retained earnings formula, a retained earnings statement lists beginning retained earnings, net income or loss, dividends paid, and ending retained earnings.
If you manage your accounting books well, you can prepare accurate financial statements. Patriot small business accounting software makes it easy to track your income and expenses online. Try it for free today!
Get up and running with your free payroll setup and enjoy free expert support. Try our payroll software with a free 30-day trial. Retained earnings are an important part of a company’s financial health, reflecting the cumulative profits, or net income, generated by the company over time after taking into account dividend payments. Shareholder. This income is considered “retained” because it is not distributed to shareholders as dividends but rather is reserved by the company for future use.
Can’t Get The Correct Retained Profit For Next Accounting Period
Retained earnings are important to investors and financial analysts because they provide insight into a company’s long-term growth potential. A company that maintains a high level of profits indicates that it has been able to generate consistent profits and use them to reinvest in the business or fund future growth opportunities.
The retained earnings formula provides the following method:
What is retained earnings accounting, what are retained earnings, what does retained earnings mean in accounting, what are retained earnings in a balance sheet, retained earnings definition accounting, what retained earnings, retained earnings in accounting, retained earnings accounting entry, retained earnings meaning in accounting, what are retained earnings on balance sheet, retained earnings accounting equation, accounting retained earnings formula