What Is The Difference Between Common Stock And Preferred Stock – The difference between common stock and preferred stock Investors in preferred stock do not have voting rights, but can receive dividends regardless of whether the company is profitable. In contrast, investors who own common stock can vote but may or may not receive dividends.
Both common and preferred stocks are popular in the options market. Explain the main differences between common and preferred stock.
What Is The Difference Between Common Stock And Preferred Stock

Investments made by business owners are not guaranteed returns. The capital of the owners of the company.
How To Hack Angel Investing: Terms — Republic
Equity refers to the capital invested in the business, excluding borrowings. Share capital is called stockholders’ equity.
Preference capital includes shareholders’ equity, but its characteristics are different from equity capital. It has both elements of debt.
Preferred stockholders do not have voting rights for directors and therefore do not participate in voting rights.
If the company’s performance is poor, shareholders are not entitled to receive dividends. Shareholders bear the risks of the business and share in both the company’s profits and losses. When a company is liquidated, investments must be made if the realization of the assets does not meet the liabilities. Shareholders should receive dividends.
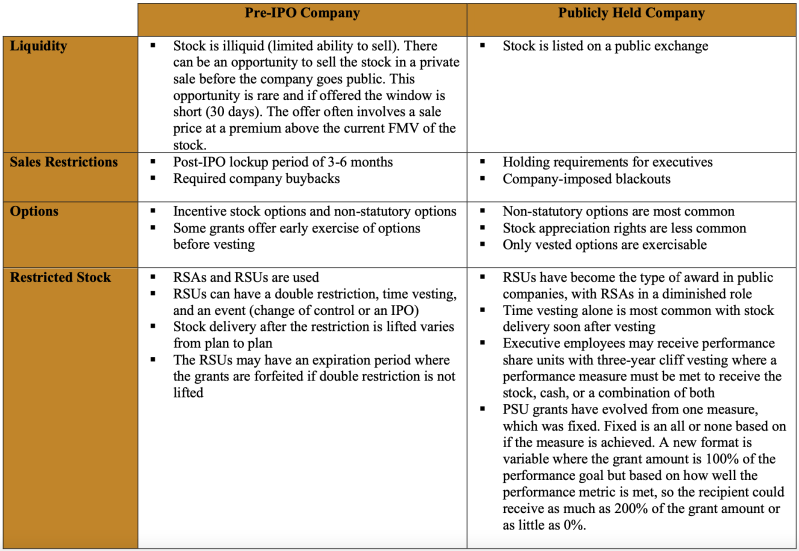
Equity Compensation Plans: Pre Ipo Companies — Scott Oeth Wealth Management
A company’s performance has nothing to do with its profitability. Regardless of your business scenario, you are entitled to a fixed rate of return. If the company has high profits, the board should approve additional dividends to the preferred shareholders.
Both common and preferred shares constitute the capital of the company and are the beneficial owners of the company. Most days the importance of preference shareholders is decreasing and very few companies use preference share capital for their operations. Although shares are an important part of a business, preference shares are issued to obtain certain tax benefits or to restructure certain corporate debt. For income, the D/E ratio will not improve as the amount borrowed increases. Preference share capital is used for expansion of capital expenditure, working capital needs, payments to related parties, etc.
This determines the biggest difference between common stock and preferred stock. Here we also explain the key differences between popular and recommended stocks using infographics and comparison charts. See also the following articles:

Complete Excel VBA Suite – 120+ Tutorials |: 110+ Mock Tests | 500+ hours | All life | 120+ online courses 30+ projects 500+ hours lifetime access to verifiable certificates
Cost Of Capital 4
Financial Analyst Masters Training Program 2000+ Hours HD Video 43 Learning Tracks 550+ Courses Verifiable Certificate of Completion Lifetime Access
Complete data science suite, 2000+ hours of HD videos, 80 learning tracks and 400+ courses. Verified Certificate of Completion, Lifetime Access
Universal Software Development Kit 5000+ hours of HD videos 149 learning paths 1050+ courses.
This website or its third-party tools use cookies that are necessary for its operation and are required to achieve the purposes specified in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link, or otherwise continuing to browse, you agree to our Privacy Policy. Preferred stock and common stock are two different types of stock that a company can issue, and their holders have different rights. The main differences are:
Tutorial 2 Solution
In other words, preferred stock can be thought of as a hybrid security that has characteristics of both equity (such as common stock) and debt (such as bonds). They carry less risk than common stocks (taking into account dividends and liquidation benefits), but they also have less potential reward.
Investor A buys 100 shares of TechCo at $10 per share. As a common shareholder, Investor A has voting rights in TechCo and is entitled to receive dividends, but these dividends are not guaranteed. TechCo had a great year and decided to pay a $1 per share dividend. Investor A receives $100 ($1 * 100 shares).
However, TechCo has underperformed this year and has decided not to pay a dividend. As a common shareholder, Investor A receives no dividends during the year.

Investor B buys 100 shares of TechCo preferred stock at $20 per share. Preferred stock pays a fixed dividend of 5% annually. This means that Investor B is guaranteed a $100 dividend ($20 * 100 shares * 5%) each year.
Preferred Stock Definition
Even if TechCo had a bad year and didn’t pay any dividends to its common shareholders, Investor B would still receive a $100 dividend because the preferred dividend is guaranteed (assuming it’s not a deferred dividend).
Also, if TechCo were to liquidate, Investor B would be paid after debtors and creditors and Investor A. However, Investor B, unlike Investor A, generally does not have voting rights at TechCo’s shareholder meetings.
This simplified example allows you to see the different rights and potential benefits of common and preferred stockholders. It is important to note that the actual situation is more complex and may vary from company to company. Be sure to read the promotional terms before investing.
Check out one of our free Study Hacks tutorials to learn the free study techniques that have helped thousands of test takers crack sections faster and avoid mistakes… Tickets for company property, not digital records these days. Ownership of common stock allows you to influence company decisions by voting on board of directors and company policies. In the long run, these types of stocks can offer attractive returns. But keep in mind that this has its pitfalls. If a company has to liquidate its assets, common stockholders are at the end of the line and can only receive compensation after bondholders, preferred stockholders, and other creditors get their shares.
Read In One Picture
The cost of common stock issued is shown in the stockholders’ equity section of the company’s balance sheet.
Common stock is basically a form of ownership in a corporation and represents a right to a portion of the company’s assets and profits. If you’re a shareholder, that means you’re a “part owner,” but that doesn’t mean you own the company’s physical assets, like chairs or computers. They belong to the company itself, which is a separate legal entity. Instead, as a shareholder, you have a residual claim on the company’s profits and assets. This means you are entitled to whatever is left after all other debts are paid.
When traded on a stock exchange, common stock can be bought and sold by investors and traders, and common stockholders are entitled to receive dividends if declared by the company’s board of directors. They are usually paid out of the company’s profits, and the board of directors decides how to distribute them, taking into account factors such as the company’s performance, future capital requirements and broader financial goals.

The first ordinary shares were issued by the Dutch East India Company in 1602 and traded on the Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Over the next four centuries, stock markets were established around the world, with tens of thousands of companies listed on major exchanges such as the London Stock Exchange and the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
Chapter 20 Long Term Debt, Preferred Stock And Common Stock.
Large-cap stocks in the United States are traded on public exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. As of mid-2023, approximately 2,300 stocks are listed on the NYSE, with another 5,700 listed on other US stock markets, making the NYSE the world’s largest market by market size. Smaller companies that cannot meet the listing requirements of these major exchanges are considered private and their shares are traded over the counter.
Preferred stock is another type of stock that offers different rights than common stock. Both types give ownership of the company, but preferred stockholders have greater rights to the company’s assets and dividends than common stockholders. This elevated status is reflected in the name “preferred” shares.
Both common and preferred stock allow investors to own shares in a company, but there are important differences that investors should understand.
Owners have voting rights in the company and can participate in decision-making on corporate policy and board elections.
What Is A Common Stock? Learn The Basics.
The company’s shareholders have the right to vote on important decisions concerning the management of the company. For example, shareholders vote on board members. Common stock usually gives shareholders voting rights, while preferred stock often does not.
Both common and preferred shareholders can receive dividends from the company. However, dividends on preferred stock are predetermined based on the par value of the stock or the par value plus the stock dividend rate. Companies can choose whether and how much to pay dividends to common shareholders.
If the company does not have enough cash to pay dividends to all shareholders, preferred shareholders have priority over common shareholders and are paid first. If the holder of the cumulative preference shares is unable to pay the dividend, it will be counted as a “deferred dividend” and must be paid before the dividends are paid to the common shareholders.

Open Market Trading of Common and Preferred Shares. Investors can choose to buy or sell any type of stock.
Traditional Stocks Vs Shares Cfd
However, investors typically trade common stock rather than preferred stock.
Difference between common and preferred stock, what are the key differences between common and preferred stock, what is the difference between delta economy comfort and preferred, difference preferred and common stock, what's the difference between common stock and preferred stock, what is the difference between common and preferred shares, the difference between common and preferred stock, explain the difference between common stock and preferred stock, what is the difference between common stock and preferred stock, difference between common and preferred shares, difference between preferred stock and bonds, what is the difference between buick envision preferred and essence